Endless e-commerce startups launch each day, but not all of them go on to be successful.
Undoubtedly, online stores are the goldmines used by wise entrepreneurs for years, yet we see so many new ventures fail because they miss out on the critical aspects of e-coms.
One of the most common flaws among the startups that don’t make it to the top is the improper implementation of the Google Tools like Google Analytics and Google Webmaster.
What is even more surprising about the startups that don’t do well is how they lack Google Ads, Google Tag Manager, and Google Merchant Center services.
These five Google Tools are irreplaceable for any online business today, and with this post, we aim to educate young business owners about them.
Instead of throwing around all the technical and geeky words at you, we have decided to make it a straightforward and comprehensive beginner’s guide. Let us first start with the tool of Google Search Console.
-
Google Search Console — Keeping Track of Website Performance
You cannot expect people to improve their store’s online presence if they do not know how their site is performing. The Google Search Console helps you understand how well your site is doing and aspects that need more work.
With the power of Google Search Console, you get to know your site’s performance-related issues, including the notorious crawl errors and a lot more. The GSC emails timely warnings that may be affecting your e-commerce website, which, in turn, gives you a chance to fix it and avoid a drop in your site performance.
You also get to see the measure of your site’s performance with the factors like Clicks, Average Click Through Rate, and many other helpful parameters that we’ll discuss below.
-
Setting Up An Account on the GSC
The first step to getting started with Google Search Console is by creating an account.
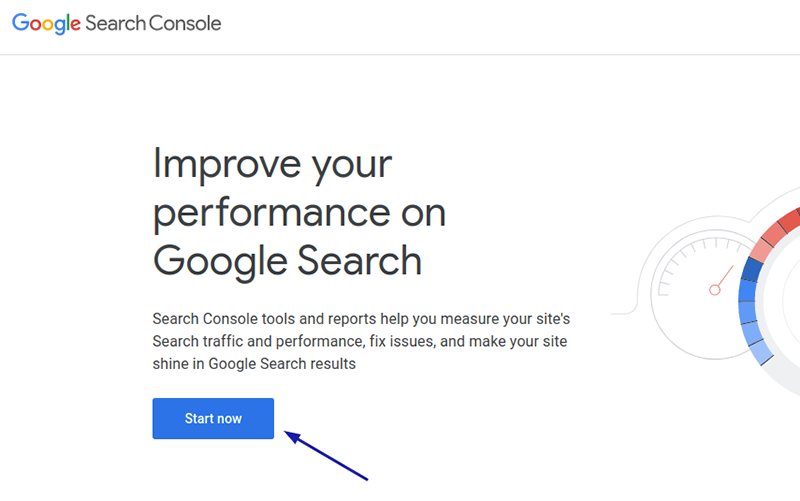
- When you head over to the GSC tool site, click Start Now and continue to sign up or log in with your Google account.
- Once you log in, the following page will appear.
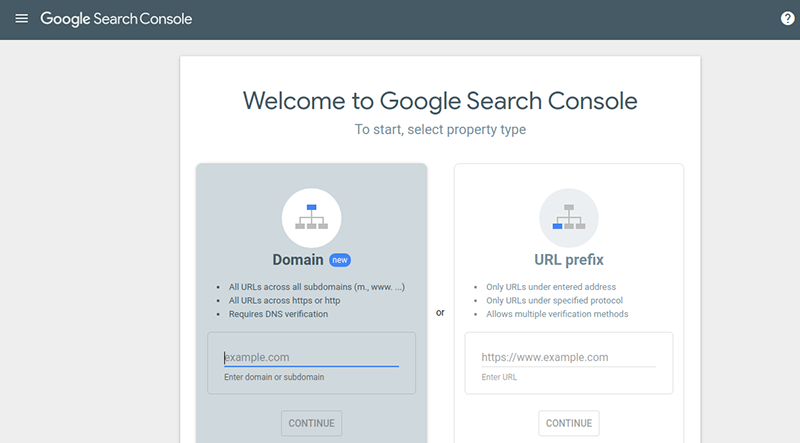
- Adding a property: The page asks you to add a property (your site) to your Google account. There are two ways you can do this. One by using the ‘Domain’ option, and the other by the ‘URL Prefix.’
- To be real here, even the most technical people don’t use the Domain option to add their site as property because it requires a DNS verification, which is a tedious task.
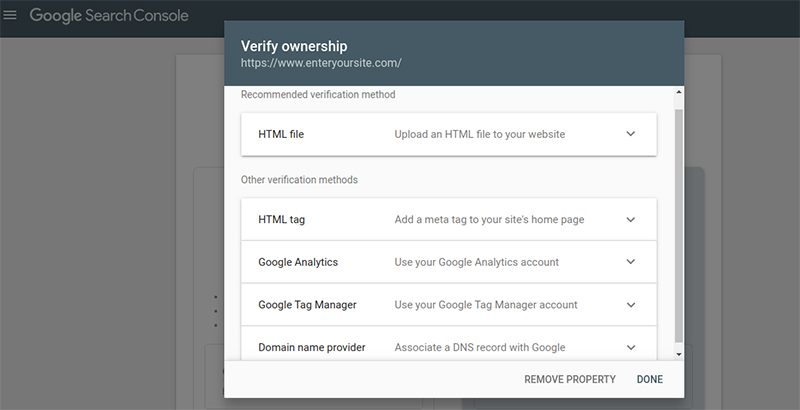
- Using the URL prefix option, you get to choose at least four ways to verify that you own the site, which is way simpler than a DNS Verification. The simplest of them being HTML Verification.
- Verification with HTML Tag:
Head over to the URL Prefix and type in your site’s name. You’ll be asked to verify your ownership with different options. Here, you can click the ‘HTML Tag’ option and copy the code on your screen.
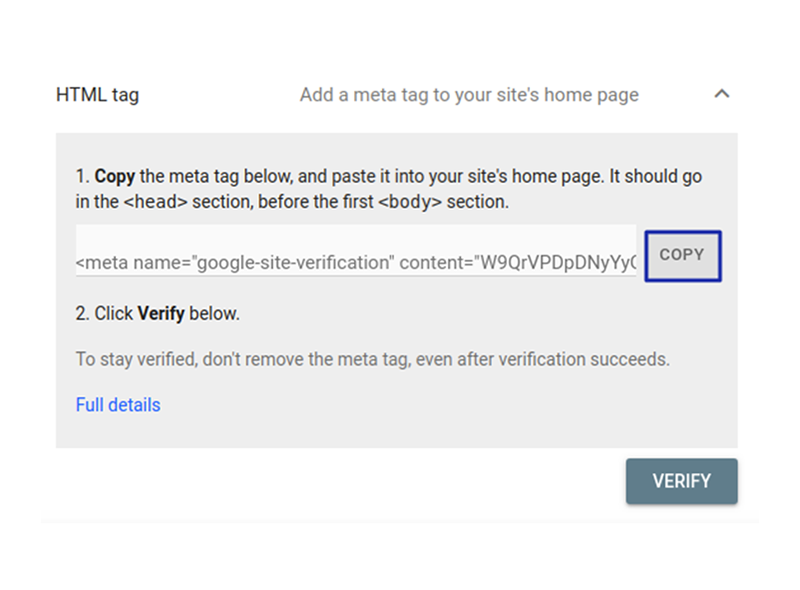
Head over to any page on your site and launch its HTML editor. Under the head tag, <head>, of your webpage, paste this code, and you are all set to go.
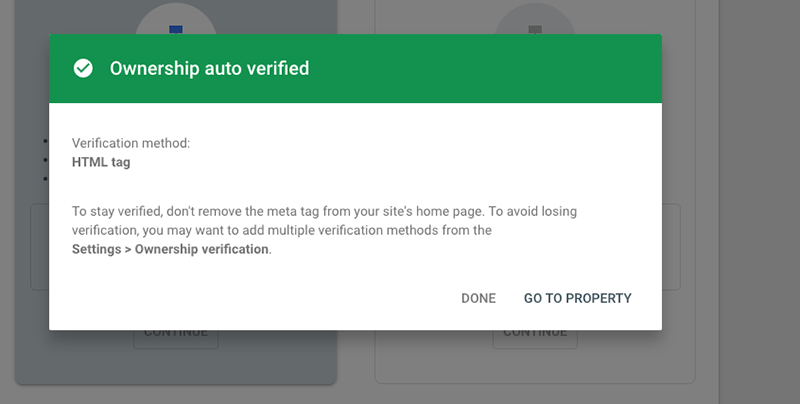
Go back to the search console, click ‘Verify,’ and voilà! You have now successfully verified your property/ site on the Google Search Console.
- The other methods of verification include:
- Verification with Google Analytics – If your e-commerce website has a verified Google Analytics account, you can log in to the GSC with that account and continue to verify your property with a single click.
- Verification with Google Tag Manager – Same as Google Analytics, if you have a Tag Manager account associated with your site, log in to the GSC with it and go on to verify it with a single click of your mouse.
- Verification with the Domain Name Provider – When using the DNP option, Google provides you with a verification text. You must paste it to the DNS configuration of your site. Make sure to sign in to the account you have with your domain name provider when using this method. (It is better off to use the other three methods.)
-
Understanding the Google Search Console
Once you have verified your site’s ownership to the GSC, you will see an overview of your site’s different parameters on the portal. The most crucial of these are:
Performance:
The performance tab contains factors like total clicks, total impressions. Along with these vital stats, you can also view average CTR and average position here.
- Total Clicks, as understandable from the name, is the no. of clicks that the search results from your site have achieved. It helps you understand what pages of your e-commerce are most clicked from the Google SERP.
- Total Impressions: The total impression factor lets you know the number of times your site was viewed on the SERP of Google. It gives you a measure of your site’s visibility whenever users enter their search terms relevant to your e-commerce.
- Average CTR: The percentage of people who came across your site on the SERPs and clicked is mentioned under average CTR. If the CTR of your website is lower than what you expect, then it may be an excellent time to add meta tags to your pages that make the users click your links.
- Average Position: Depending on how high or low your site has ranked on the searches, you can know its average position with this factor. It also tells you the average position of specific pages by browsing them below the graphical table.
URL Inspection:
The URL inspection tool allows you to go to the search bar and check the page of your interest. So, if there is a specific page on your site that you want to check for the last crawl, whether it is indexed or not, and check the referring pages to it, then the URL inspection will come in handy.
Index:
The index section lets you check your site’s coverage on Google’s search engine. It tells you how many pages of your site are indexed on Google. It is a great way to find out which pages of your site haven’t been crawled by the Googlebot and for what reasons. The GSC tells you why it hasn’t crawled some of your site’s pages and that, in turn, can let you fix them. These are commonly 404 errors that can be fixed once pointed by the GSC.
The other tools under the GSC index section allow you to submit and view sitemaps and remove any pages that you may not want Google to index on its SERP.
Enhancements:
Under the Enhancement tab, you can view the Vital Core Stats of your site. The stats under these tabs more or less give an insight into the desktop and mobile site speeds.
If you do not have the GSC set up for your site, and are still looking to gather this parameter’s data, then the PageSpeed Insight Tool from Google may be of some help.
Links:
The link section in the GSC lets you know which sites are linking to your e-commerce site. You get to know the anchor texts and the link to your pages that the sites are using and how many times these sites have linked to yours. It is a helpful way to keep track of links to your site to create a healthy backlink profile.
-
Google Analytics — Understand Your Visitors Better

What if you get the power to understand your customers better? Imagine how much better you would be able to sell your products if you can know the age, gender, and location of the people who are visiting your website.
With Google Analytics, you get to know all this and much more. First, let us tell you to set it up on your site.
-
Setting Up Google Analytics for Your Site
The easiest way to set up a Google Analytics account for your site is by adding the tracking code to your site’s source code.
- Start by signing in to Google Analytics using your Google account.
- Once logged in, you will see the following screen.
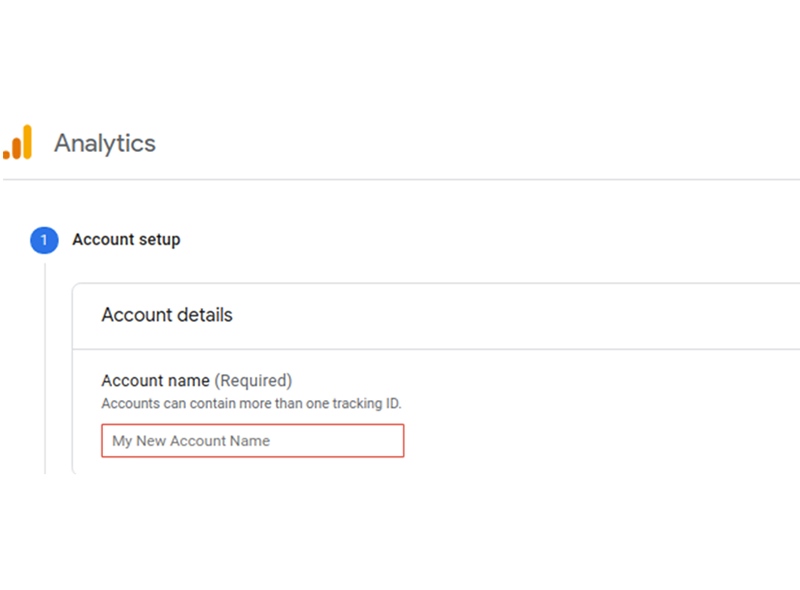
- Enter an account name of your choice, and continue.
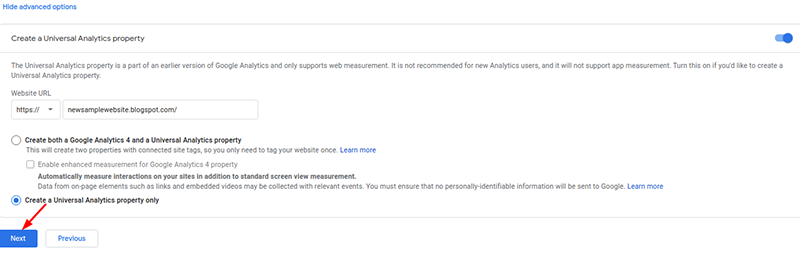
- The next step is to enter your site address in the property name box. Before you click next, click the advanced option and switch on the button on the right of the ‘Create a Universal Analytics property’ option.
- Enter your site URL and continue to create a Universal Analytics property only by choosing the option and clicking next.
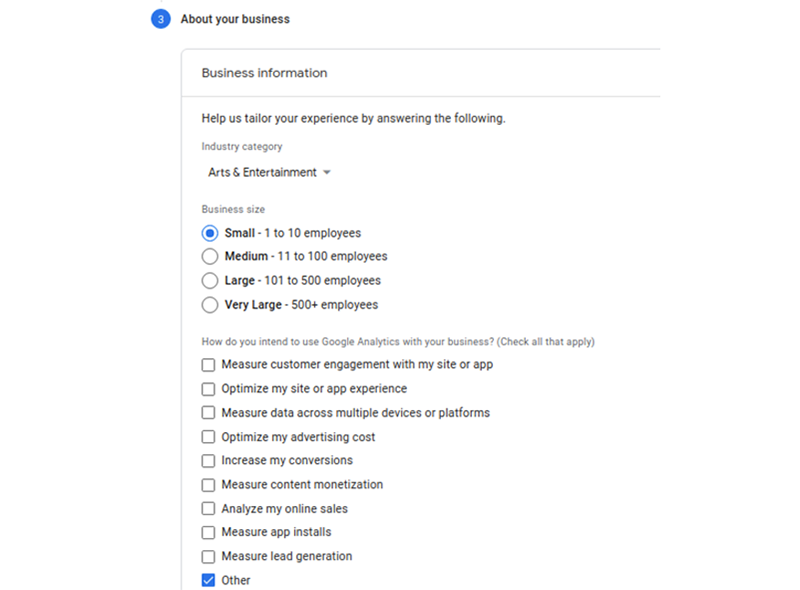
- Choose your preferred option of industry category and how you would like to use Google Analytics for your business. Hit the create option, and agree to the conditions by Google Analytics.
- The page will refresh, and you will see a Google Analytics Tracking ID along with a Global Site Tag on your screen. Copy the code under your site’s head tag, and you are all set to use Google Analytics for your site.
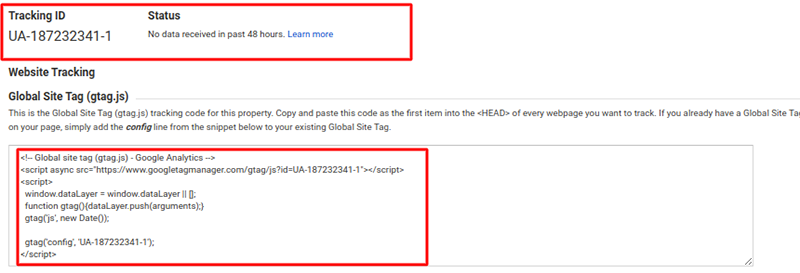
Within the Google Analytics dashboard, you’ll uncover a lot of useful information on your site that you may otherwise not be able to.
- The real-time option gives you a comprehensive overview of the current website traffic sources and where they are based from the location section.
- Audience reports in Google Analytics ensure that you stay up-to-date with the user demographics, their age, interests, the kind of devices they use to be on your site, along with a whole lot of other information. It helps you understand your site visitor or potential customers better.
- The acquisition section in Google Analytics lets you know how the customers are reaching your site. You get to know whether your Google Ad campaigns are effective or your social media strategy needs improvement to add traction to your site. It is a great way to understand which platform your visitors are coming from and then target them.
- Behavior is an interesting section of Google Analytics that can also help the eCommerce site owners. It tells you how people engage with your website. Understanding how the users navigate your site and reach your interest page can be a great way to divert the traffic from other pages towards it.
For e-commerce, this section becomes particularly useful as they can use strategies like adding links to the blog section that is receiving traffic to the product pages. Along with these massively informational stats, you get insights into the site speed, content, and the searches that take place on your website.
- The events section comes in handy to know the pages and the buttons that the unique and regular site visitors click. You get to choose the events you want to track on your site (a video is clicked, paused, or played, for example.)
- Conversions are probably one of the most crucial stats that e-commerce sites require to improve their performance. You get to set goals with your developers or by using the Google Tag Manager to track. These goals may include the addition of an item to the cart or the completion of a purchase.
An entire sub-section is dedicated to the ‘E-commerce’ in the conversions report, where one can know the product’s performance, sales made, and even purchase time.
-
Google Tag Manager – Making Tracking Easy for Non-Coders

Trust us; not every SEO specialist knows hardcore coding. Yes, it is a great advantage to have if you carry this skill, but to track your site usage better on the analytics, GTM is enough to help you.
The various tags that GTM lets you use for your site also help you with other platforms like Google Ads and many more. You can do all of it without having to learn a great deal about website development or javascript. The Google Tag Manager interface enables the site admins to create tags for different events that they want to track on platforms like Google Analytics without having to code manually.
There are massive advantages that come with the GTM, the major one being – a higher accuracy in the codes made by the tool, along with the customizations that you can do to these tags.
Creating a Google Tag Manager Account is easy and can be done as we explain below.
-
Setting Up Google Analytics for Your Site
- Begin by going to the GTM sign-up page and click “Start for Free.”
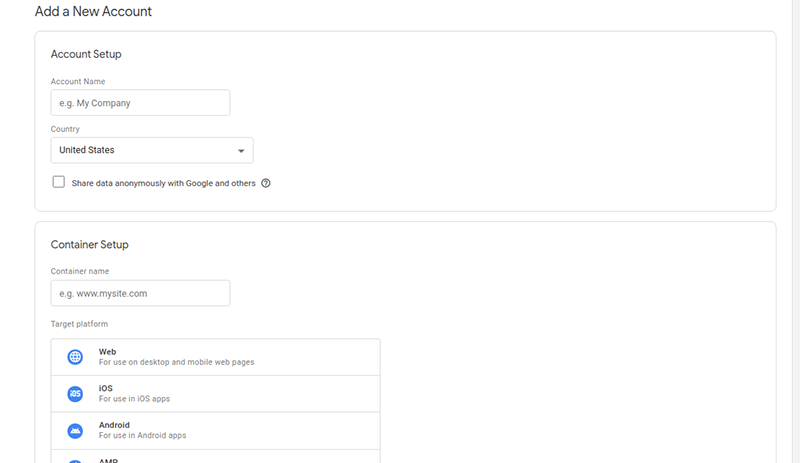
- On the account setup page, type an account name, and select your country.
- Next up, type a container name of your choice, and based on your e-commerce business, select web, android, or iOS as the target platform. Click Create.
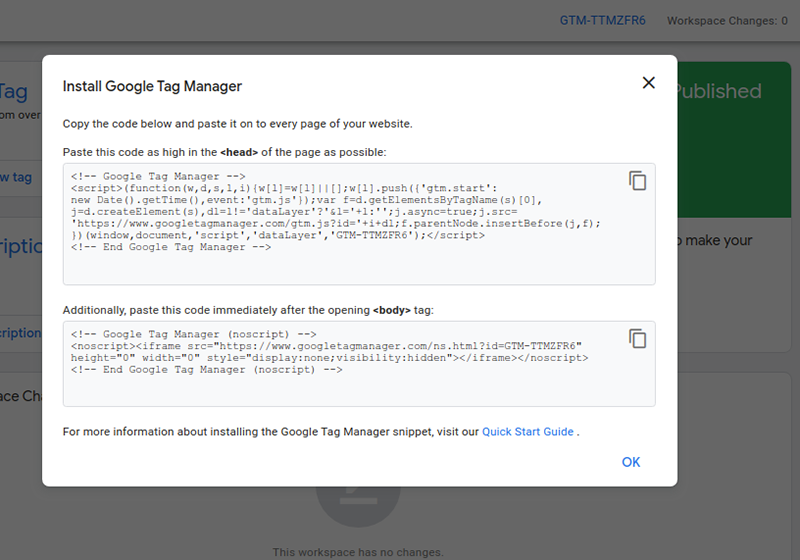
- Next, you will be greeted with a screen by the GTM that will show you a set of two codes to paste in the head and body section of your website’s source code.
- Once you paste these codes under the mentioned sections, you can go on using the GTM.
What Can You Do with Google Tag Manager?
It’s essential to understand that the Google Tag Manager is not a stand-alone tool. It works well with other tools like Google Analytics. Once you add different tags to your site with the help of GTM, it makes tracking so much simpler on the analytics. For example, you can know the newsletters being signed up on your site, an image being downloaded from it, and even more complex codes.
There are three crucial labels on the GTM that every user must know as a basic: Tags, Triggers, and Variables.
- Tags
Many third-party apps, a lot of them for site analysis, require certain code implementations to be used in the site’s source code. The Tags in the GTM help the site admins customize their codes and implement them to their website.
When you click the Tags section and browse through it, you come across numerous snippets codes popular among the users (like Pinterest or the Quora Tags). To use these tags, you must add a unique ID in their respective sections. By following this step, you can activate the tags for your account and on your site.
- Triggers
Consider triggers as a stimulus that you set for a code to execute. Before any codes submitted through the GTM can run to notify Google Analytics about an event happening, you must set a trigger for it.
- Variables
Variables are the value holders in the GTM, some of which are built-in, while the others can be defined when customized. They are like the filters for the triggers that would only set off when these variables’ conditions are met. For example, you can set a variable for a particular video or page view on your site.
4. Google Ads – Promotions Made Efficient

If you have been around the online marketing circuit for some time, you must have heard about Google Adwords. Google Ads is a powerful tool that has been helping businesses gather a massive amount of visitors daily.
The tool enables you to gather traffic from the Google Search Engine for the queries made on it and relevant for your business. From small businesses to large conglomerates, several companies have benefited from this tool to make better fortunes.
-
Setting Up the Google Ads Account
- Head over to the Google Ads Sign Up page and login with your Google Account.
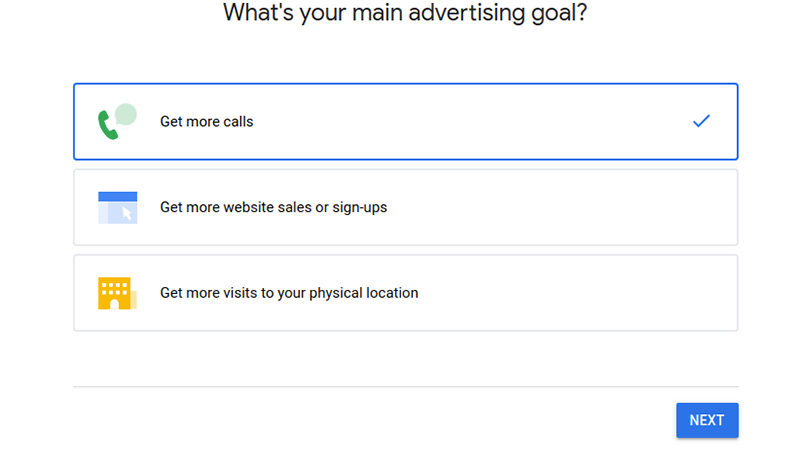
- Choose your advertising goal and click on next. For an e-commerce website, you want to ‘get more website sales or sign-ups.’
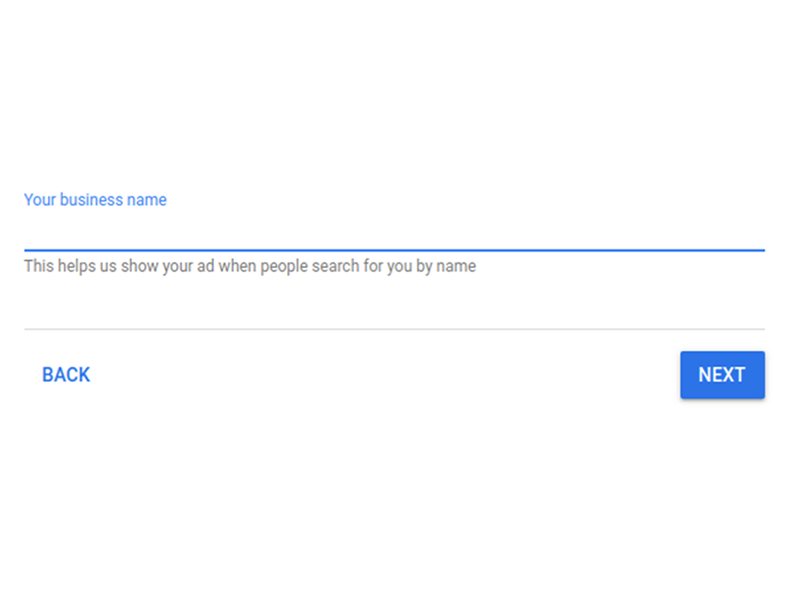
- Type in your business name and click Next.
- You will be prompted to enter your website name, type it in, and click Next.
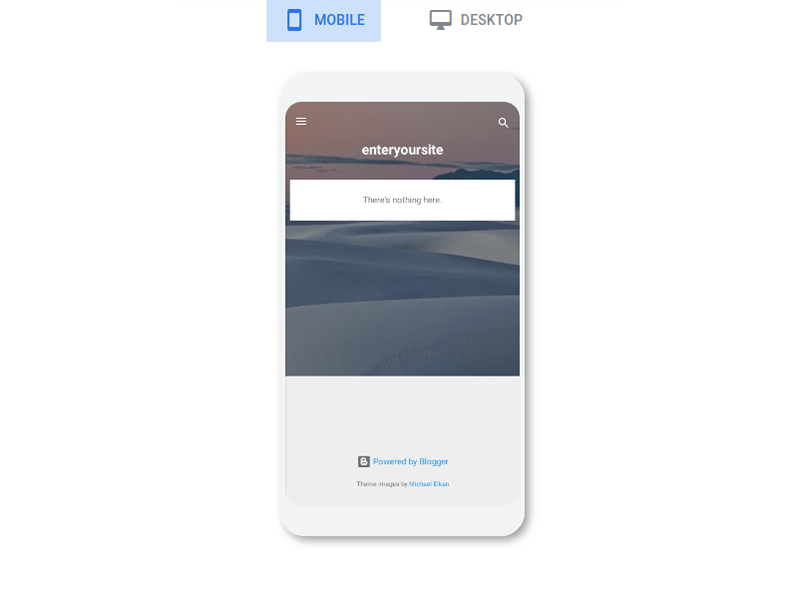
- You will be given a preview of your website for phones and desktops for your website’s landing page. Click Next.
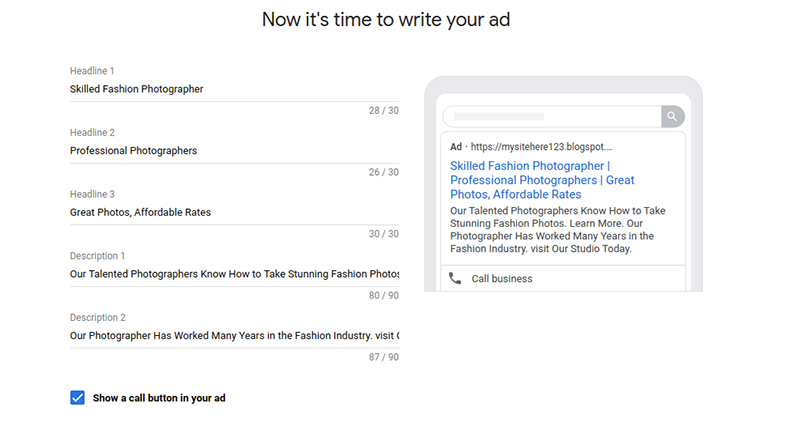
- Type in the Headlines of the product ads that you intend to run on the Google SERP and the descriptions related to them. Make sure that these ads are not misleading or violating the terms of Google. Check out what Google thinks is a useful text for Adwords.
- Add your phone number to the account and click Next.
- Continue to choose the themes of your ads from the suggestions and choose the language of your ads.
- Click Next and Choose the Geographical region that you want to target on the maps. It is at this step the knowledge of your buyer persona comes into play.
- Next up, choose a budget for your ads. Once you do it and continue further, review your ads and confirm payment info.
The budget may be any number, but do not be misled into the thought that – a higher budget will get you featured in the ads for all the keywords you target. Your chances of making it to the ads for your searched keywords have a lot to do with the combination of the quality of ads you write and the budget.
- Once the payment methods are selected, and the transaction is complete, you can check your Google Adwords dashboard and manage your ads from there.
Using Google Adwords: Get More Eyeballs on Your Brand
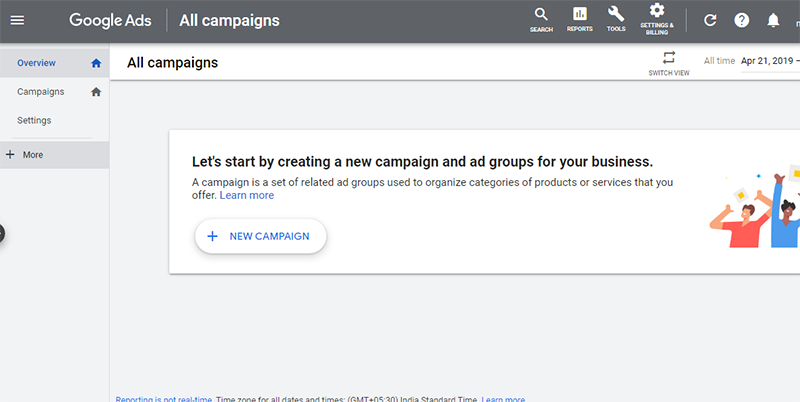
Adwords is a vast platform, and it’s common for people to be overwhelmed by it. You can avoid ending up like that by sticking to using what you need instead of getting into this tool’s technicalities.
If you didn’t realize it yet, by following the steps of signing up with Google Ads above, you would have created your first ads campaign already. You can make more campaigns based on other sets of keywords related to your products by clicking ‘New Campaign‘ on the dashboard and following the same steps. All that you need to know about ads after it is how to use its dashboard. Some major components of ads Dashboard are as follows-
- Account Overview: This is a new feature introduced by Google on the ads tool. Here, you can view all your campaigns along with trending words that are taking people to your ads. It serves as a gateway for you to glance over all your campaigns and recommendations from Google to make them better.
- Audiences: The option allows you to set a better target for your ads. You can combine different demographics, including age, locations, and many more attributes, to find your potential customers.
- Pre-defined reports: The pre-defined reports have a lot to offer compared to the ‘dimensions tab’ of the Google Ads in the older UI. You can view your campaigns’ performance and the possible opportunities in the more visual form here in the form of graphs and charts. You can choose to have information only for the activities you want to know about, like clicks and impressions.
- Other options: The other features on the ads platform are under the ‘tools’ dropdown. Here you can find options like Shared Libraries, Bulk Actions, and Measurements. Heading over to the Plannings pane will let you select keywords, know their search volumes, difficulties in the ranking, and how much the competition is paying to rank for them. You can view ad previews and diagnoses here.
5. Google Merchant Center: Shopping Ads Made Easy

Google Merchant Center is another Google tool that can have a massive impact on your products’ sales. To be honest, if you have a physical store and still not using Google merchant center to run shopping ads, then you might be missing a trick here.
Google shopping ads are more appealing, visual, and likely to score you a sale if used correctly. With the Google merchant center, you create a gateway to connect the Google AdWords campaign to your shopping ads.
As intelligent as the Google services may be, it does not understand what products you are selling, the related inventories, and other details of your services. Google Merchant center lets you send out your shopping feed to Google so that when your shopping ads campaign run, it knows what to list.
-
Setting Up a Google Merchant Account:
- Head over to the sign-up page of the merchant center and hit sign-up.
- Enter your Google account username, preferably the one you signed up for Google Ads with, and continue to type in your password.
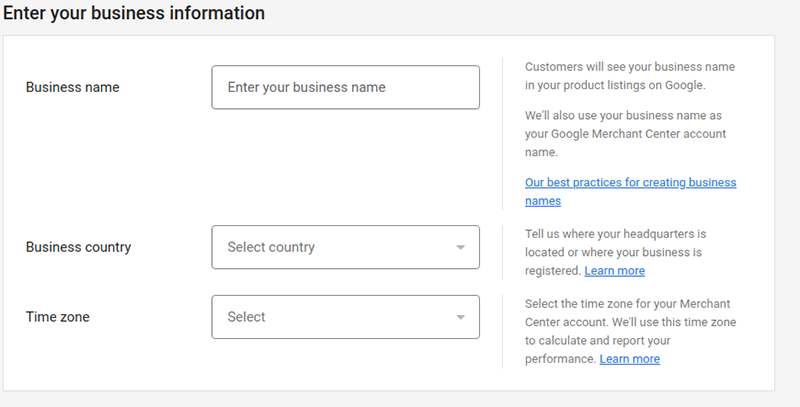
- Add your business name and country along with the time zone and continue. You will also be asked to add information about using Paypal and Shopify. Choose accordingly and continue.
- Once you reach the GMC dashboard, head over to the options (three vertical dots on the top right corner) and click ‘account linking.’
- If you signed in with your AdWords account, you would not need to go through the other process and will only have to click continue. However, suppose you are using a second account to set up Google Merchant center settings. In that case, you will need to verify your ownership of the website using HTML code snippets or Google analytics, as done for other tools earlier in this guide.
- Once verified, you are all set to add your shopping feed to the GMC.
Using Google Merchant Center
There are a handy number of ways to connect your feed to the GMC. Follow the steps below-
- Go to your dashboard’s left pane and click ‘products.’ Next, choose the feeds option.
- You can add your products to the shopping ads feed by uploading as w CSV or a text file with the right attributes to the GMC. It is a reasonably easy way to update Google about your product list.
- Other ways include using an API to connect your feed. Here, you can also use third-party plugins.
- You can also use a feed URL for dynamic updating.
Once your feed is set up, Google will start getting information on what products you are listing. It would know if the products are in stock, whether available for free delivery, and a lot of other information required for the shopping ads.
Summing Up
Aren’t these tools easy to set up? Maybe it is the lack of in-depth information out there that restricts people from using them. We hope this guide will help you use these tools correctly. So, what stops you from using these fantastic tools for your business success? Get them configured today!
Resources:
https://yoast.com/google-tag-manager-an-introduction/
https://tinuiti.com/blog/shopping-feed/merchant-center-product-feed-updates-2020/
https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/google-search-console

About the author: Vibhav Gaur, Business Head
Vibhav Gaur leads strategic operations and business growth at the organization. With a strong background in digital transformation and customer-focused solutions, he has helped numerous clients streamline their web presence and scale efficiently. His leadership ensures seamless execution across teams, with a commitment to delivering results and fostering innovation in every project.

