
Picture this: there is a digital realm where your website is not just a mere destination but a thriving metropolis- where every path is well-lit for users, every shortcut is designed to minimize speed, and every user surfing the internet can get from one point to another swiftly.
Sounds like a dream, right?
Well, not anymore, because this is achievable through a strategy called site architecture.
Site architecture is like an unseen blueprint that decides the destiny of your website and acts like a master key that opens the doors to more engagement, greater ranks, and blazingly quick load times.
But are there any benefits to site architecture, or is it just for the show?
The answer to that question would be that Google awards well-structured websites with greater ranks, faster load times, and happy customers. Thus, a well-structured site can turn clicks into conversions, whether you’re directing your audience to hidden treasures or simply improving their browsing experience.
So, are you ready to unleash the power of website architecture and increase traffic on your website?
Let’s dig in.
What is Site Architecture?
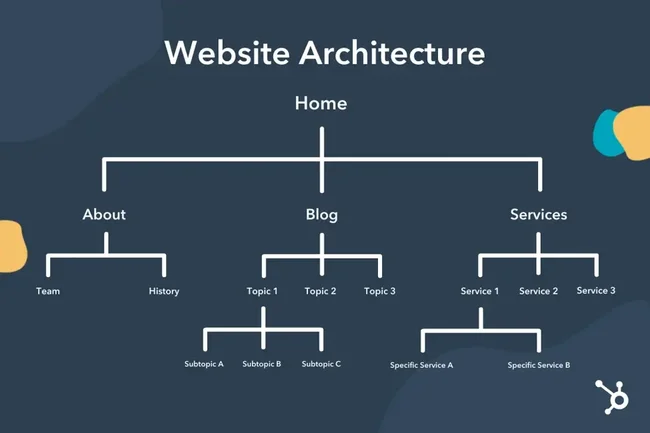
Site architecture refers to the way in which the website is built and how the various pages are linked to each other. It is the framework of a website, defining how both the visitors and search engines crawl through the web pages.
A study by Backlinko stated that a well-organized site architecture allows both people and search engine crawlers to quickly access the content they’re looking for.
A well-built site often has a template where the home page takes the users to category pages, which in turn lead to subcategories or specific content pages. Such flow makes the site easier to navigate and understand.
How Site Architecture Impacts SEO
To enhance the SEO performance of your website, consider concentrating on these crucial site structure elements.
1. Crawlability
Crawlability pertains to the ability of a search engine bot to locate content on your site. When you design your site and add a proper structure to it, it makes it easier for bots to crawl and index them. Ideally, every page should be accessible from the homepage with no more than three clicks.

For example, HubSpot reorganized its entire blog infrastructure according to the topic cluster model and started seeing improvements in search rankings for various keywords across the HubSpot Blogs.
On the other end, a poor structure can result in what is referred to as orphan content, where there are pages that are not linked by an internal link, broken link, or duplication of content.
These could exclude some or all of your web pages from the search engine index, which is not suitable for your website’s SEO performance.
How to Improve Crawlability
- Create A Logical Hierarchy:

Make sure that users are able to navigate from one page to another, starting with the homepage, categories, and subcategories.
- Use Internal Linking:

Establish connections between associatively related content and help both users and search bots navigate through your website.
- Submit an XML Sitemap: An XML sitemap is a structured guide to all the pages on your site that the search engine needs to crawl. Following is an example of an XML sitemap:

2. Indexability
A page may not be indexed even if search engine crawlers are able to reach it. Indexability is defined as whether a web page can be stored in a search engine’s index or included in search results.
One such study by Google claims that the hundreds of billions of online pages in its search index amount to more than 100,000,000 gigabytes in size. Therefore, your pages need to adhere to best practices, such as clean architecture, in order to compete and get indexed.
Certain site architecture mistakes can result in pages being excluded from search engine indexes.
- Excessive Use of JavaScript: Search engine bots may have trouble understanding JavaScript-rendered content.
- Duplicate Content:

If the exact text is on two different pages, some of the pages will not be indexed by search engines.
How to Improve Indexability
- Canonical Tags:
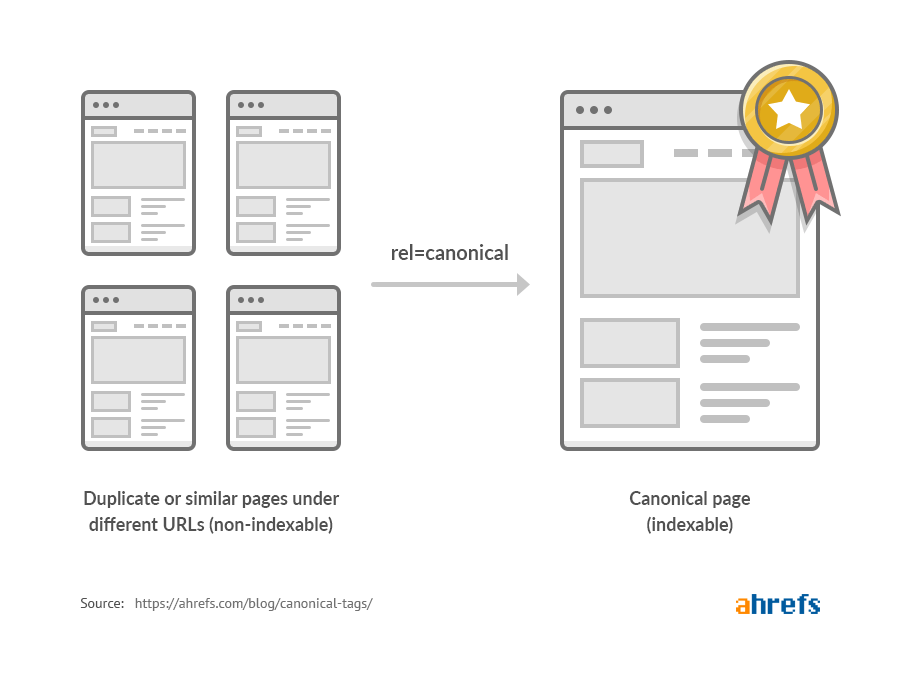
When there are multiple versions of a page, use canonical tags to inform search engines which version should be indexed.
- Optimize Site Speed: Some websites take a lot of time to load or have technical problems; these can affect the indexing done on a website, so enhance loading time and performance.
3. Site Speed
Site speed is a very important ranking factor, and the structure of the website contributes to the amount of time it will take for the page to load.
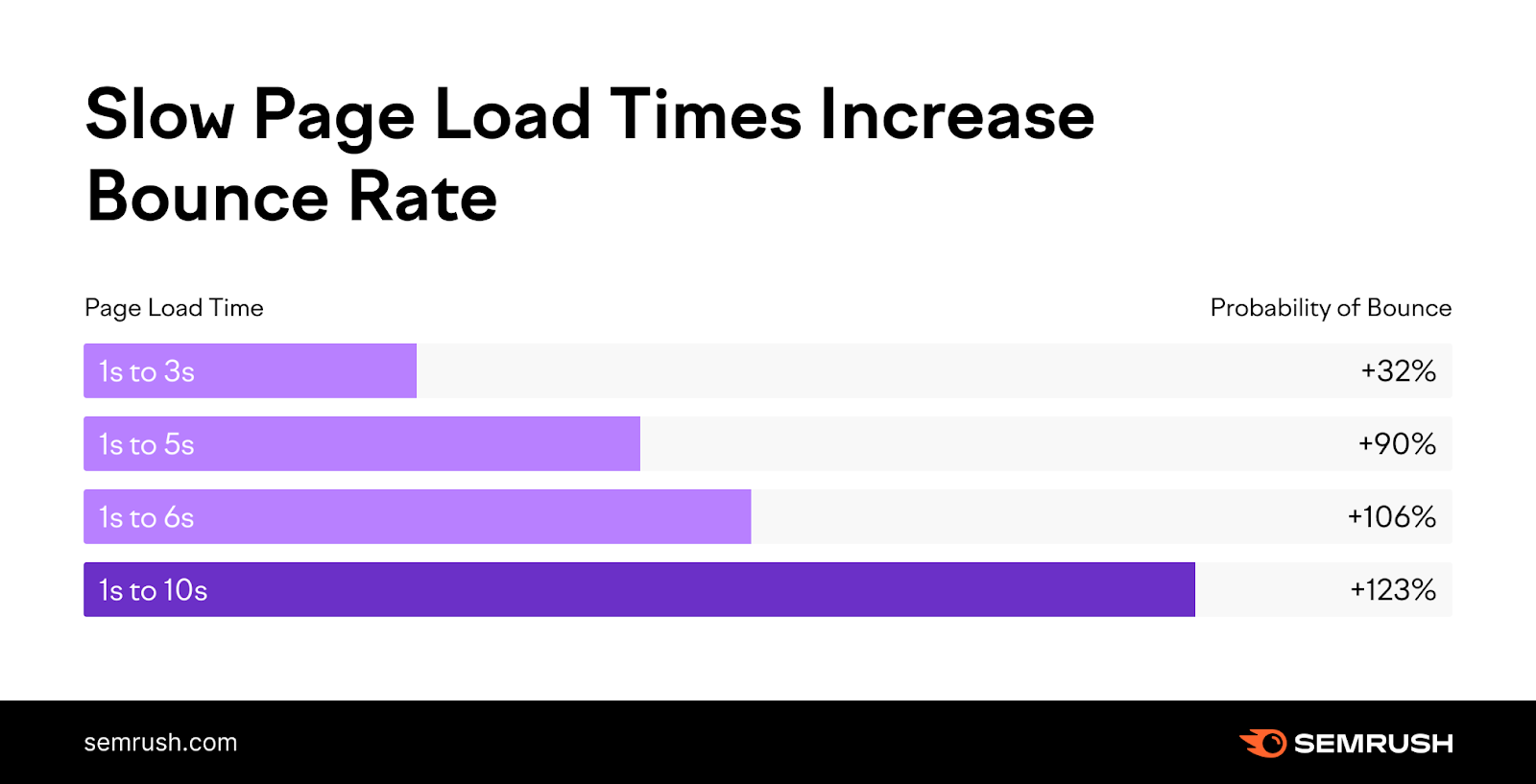
One study by SEMrush indicated that a user is three times more likely to bounce (i.e., leave your page) if your page takes longer than three seconds to load.
A slow site can result in high bounce rates, low dwell time, and low traffic to your site, depending on your position on SERP.
This includes the speed of the server, large picture or video files, and too many requests that the website places on the browser. A well-designed architecture minimizes these effects, thus enhancing performance.
How to Improve Site Speed
- Optimize Images: Shrink the image size without affecting the quality of the image.
- Minimize Redirects: Several redirects make the loading time longer.
- Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):

CDNs create cached copies of your website on servers, no matter where your visitors are located.
4. Mobile-Friendliness
Mobile-first indexing has thus become a norm in 2024. This means that Google mainly focuses on the mobile version of your site when it comes to ranking and indexation.
Going further, it has been stated that if a website were not designed for smartphone usage, it would rank low in the results no matter how well it was optimized for the desktop version.
Mobile site architecture should put an emphasis on ease of use, quick load times, and clear navigation. If people have trouble navigating your mobile website, Google will notice.
How to Improve Mobile-Friendliness
- Responsive Design: Choose a layout that changes automatically to different screen sizes.
- Easy Navigation: Steer clear of lengthy dropdowns and crowded menus.
- Remove Obtrusive Pop-ups: Google may penalize pop-ups that interfere with the mobile user experience.
5. URL Structure
One component of site architecture that is frequently disregarded is URLs. Both people and search engines can better comprehend a page’s content when the URL structure is clear and descriptive. Additionally, it affects ranking as Google views terms in URLs as a little ranking component.

According to Backlinko research, short URLs often have a little advantage in Google search results.
The Best Ways to Structure URLs
- When Separating Words, Use Hyphens:
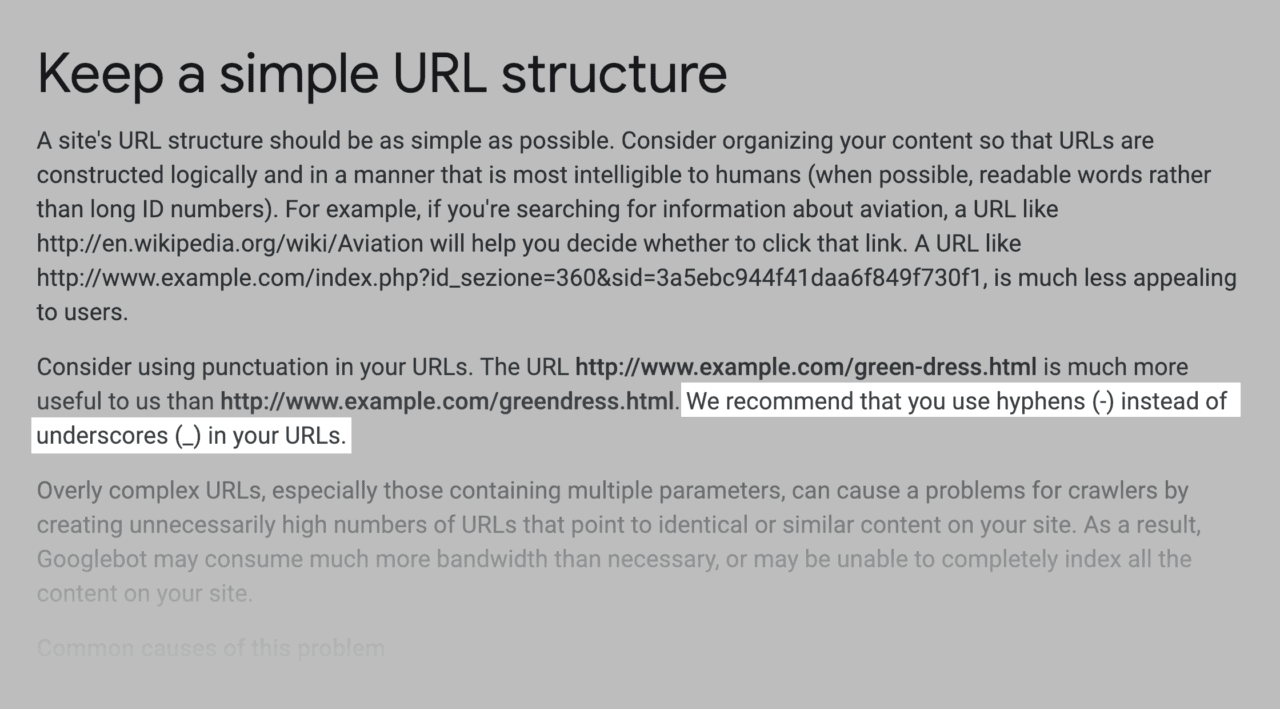
Google ignores underscores while treating hyphens as spaces.
- Keep URLs Brief And Descriptive: URLs should provide a clear indicator of the page’s content.
- Use Keywords:

Don’t overuse significant keywords in the URL, but do include them when suitable.
6. Structured Data and Schema Markup
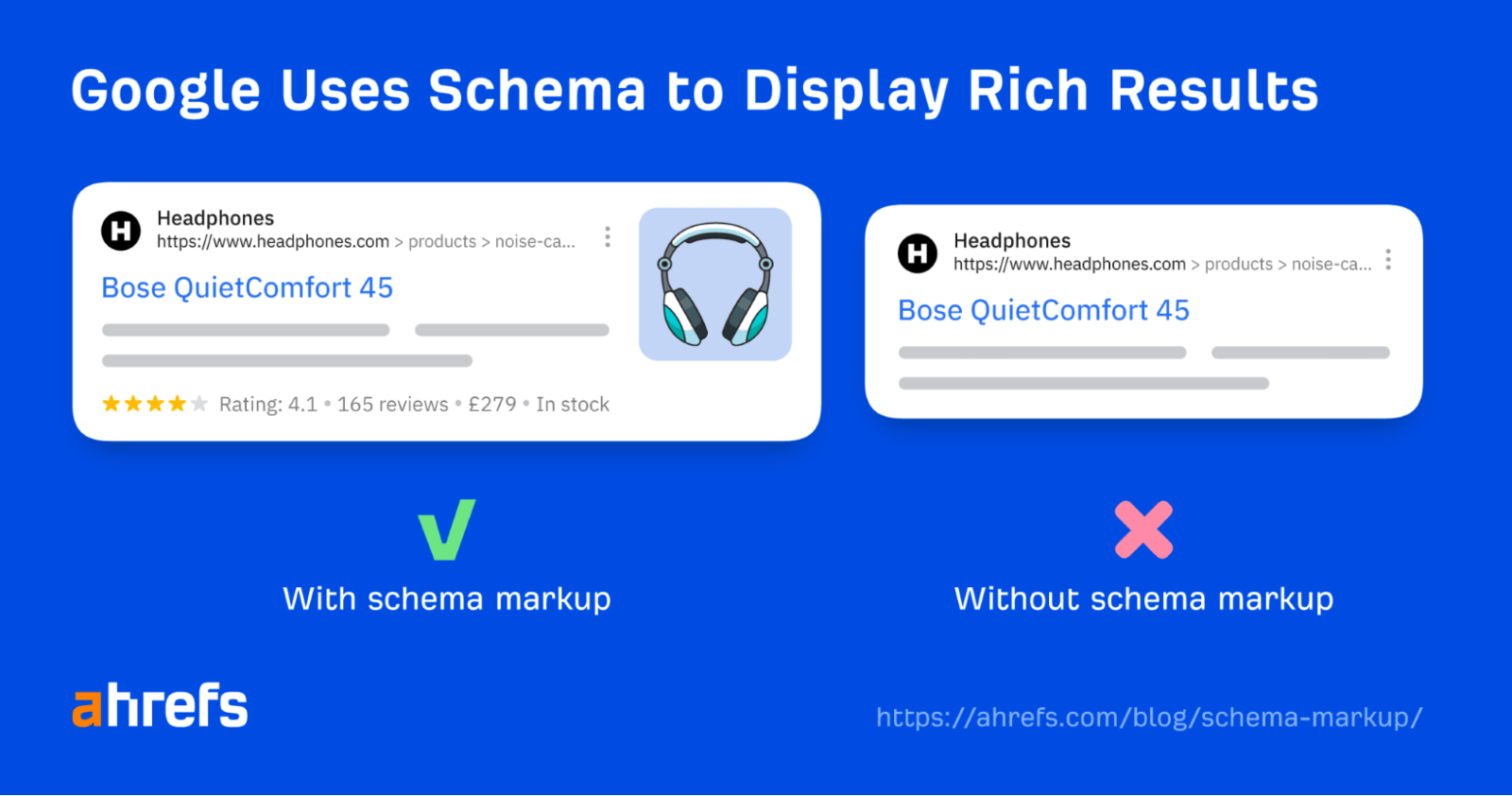
A type of microdata called schema markup can be incorporated into your HTML to improve search engines’ comprehension of the content on your sites. You can give your sites more context by utilizing structured data, which aids search engines in producing more comprehensive results.
Schema markup, for instance, enables components like reviews, goods, or events to show up as rich snippets in search results. Users find rich snippets more appealing, which might increase their click-through rate (CTR) and indirectly improve their SEO.
How to Use Structured Data
- Put The Schema for Critical Content into Practice: For crucial components like reviews, articles, goods, or local company information, provide structured data.
- Utilize the Structured Data Testing Tool from Google: Make sure search engines understand and apply your schema markup appropriately.
- Track Rich Snippets: Pay attention to how frequently your rich snippets show up in search results and, if needed, modify your approach.
Best Practices for Building an SEO-Friendly Site Architecture
Now that we’ve covered how site structure affects SEO, let’s look at some best practices for creating a website that is both search engine and user-friendly.
1. Plan Your Hierarchy Before Building the Site
The structure should be planned out before a website is created. Consider your website as a pyramid, with the homepage at the top and various pages, sections, and subcategories at the base.
Important Points to Remember
- Make Sure There Is a Logical Flow: Both users and search engines should have no trouble moving from general categories to more specialized content.
- Restrict the Depth: For optimal crawlability, no page should be more than three clicks from the homepage.
2. Optimize for Mobile-First Indexing

Making your website mobile-friendly should be your first focus, mainly because mobile-first indexing is increasingly the norm.
Important Points to Remember
- Put Speed First: Slow mobile load times might result in lower rankings and an increase in bounce rates.
- Make Navigation Easier: Since mobile screens are smaller, your website’s menus should be simple to find and use.
3. Implement a Clear URL Structure
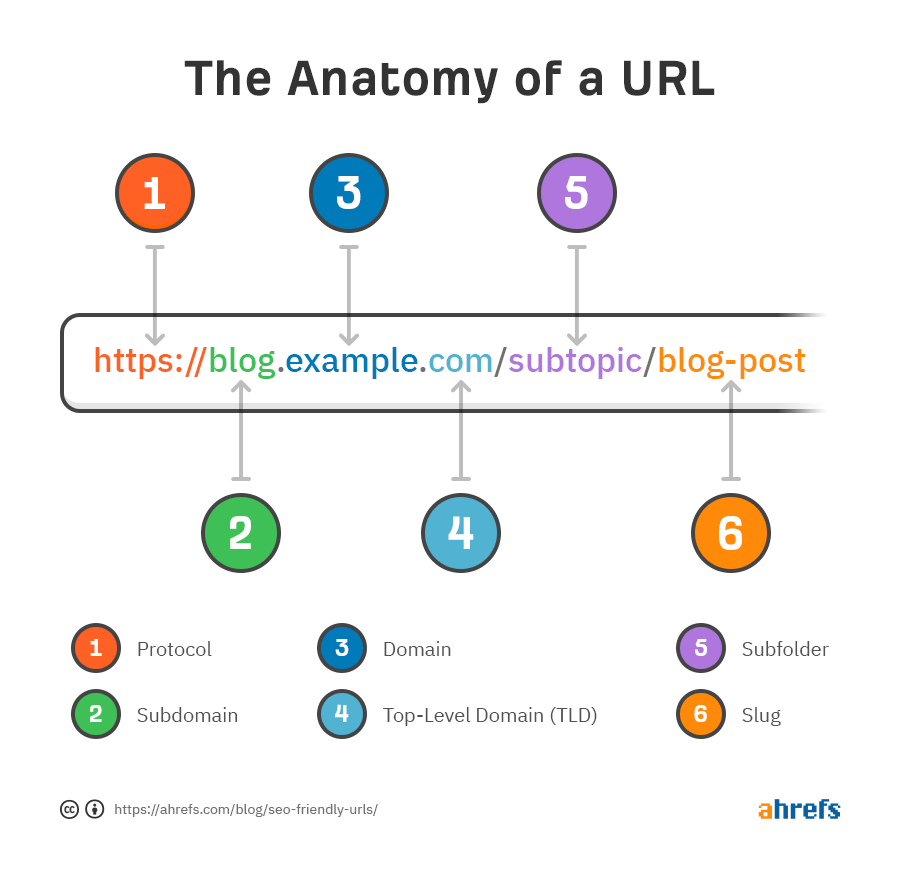
A well-structured URL improves user experience in addition to aiding search engines in comprehending a page’s content.
Users are instantly aware of what to anticipate from a website when they see a clear, informative URL. On the other hand, URLs that are too long or complicated may come off as unfriendly and confusing.
For instance, use yourwebsite.com/best-laptops-2024 rather than yourwebsite.com/page1. This makes the website more understandable for people and makes it easier for search engines to determine the purpose of the page.
4. Use Schema Markup
Spreading link equity, or “link juice,” throughout your website and assisting visitors and search engines in finding fresh material depend on internal linking.
Search engines can more easily crawl and rank essential pages when they are easily accessible from various areas of the website, which is ensured by a strong internal linking strategy. Here is an example of schema markup:

How to Build a Strong Internal Linking Strategy
- Link from high-authority pages
- Use relevant anchor text
- Ensure balanced link distribution
5. Monitor and Adjust Regularly
SEO is a continuous procedure. Utilize tools such as Google Search Console to track the crawlability, indexability, and user experience of your website. You can maintain your competitiveness in search results by upgrading your site architecture on a regular basis.
Craft Your Path to SEO Success!
Site architecture is a crucial component of SEO that is sometimes overlooked but is essential to the success of your website.
Keep in mind that a well-structured website provides consumers with a smooth, engaging experience that encourages them to return, in addition to aiding search engines in crawling and indexing your content.
A speedier, more user-friendly website is essential in today’s cutthroat digital environment, and this will eventually improve SEO and boost business performance.

About the author: Vibhav Gaur, Business Head
Vibhav Gaur leads strategic operations and business growth at the organization. With a strong background in digital transformation and customer-focused solutions, he has helped numerous clients streamline their web presence and scale efficiently. His leadership ensures seamless execution across teams, with a commitment to delivering results and fostering innovation in every project.
