Have you ever considered how many internal links you should put on your website? It’s similar to discovering the ideal amount of seasoning for a recipe. If you use too little, it will be bland; if you use too much, it will be overbearing.
Have you ever considered how many internal links you should put on your website? It’s similar to discovering the ideal amount of seasoning for a recipe. If you use too little, it will be bland; if you use too much, it will be overbearing.
Finding the right balance between an excessive number of links and not enough is similar to the skill of fine-tuning a website, which is a necessary element of a compelling online presence. As proper seasoning improves a meal, so too can the best positioning of internal links lead to a productive and easily navigated website.
Come along as we examine the subtleties of internal linking and how they affect search engine optimization for websites. All set to enhance the taste of your website? Now, let’s get started.
What are Internal Links?
The virtual corridors that connect pages on a website are called internal links. These types of links seamlessly connect various pages of a website, integrating into content as well as navigational menus. As per the Databox reports, equal efforts are put into crafting both internal and external links by 42% of SEO experts.
Their primary objective is to boost the user experience by offering them simple access to important information. For instance, through internal links, the audience can access extra information on a particular topic or relevant content. These links not only help in navigation but also facilitate the logical structure of the website.
Think of internal links as the behind-the-scenes architects who make sure the audience can seamlessly navigate the virtual environment you have designed.
Types of Internal Links
There are many types of internal links, which we have discussed below:
1.Navigation Links
The links in your website’s main navigation menu are the most significant internal links on your website. These are always included in the header of your website and let visitors know where they are in the hierarchy. They are often arranged according to product categories, main services, or important subject areas.
When a person lands on your website, these internal links let them know which pages are the “next most important.” The reason they function so much like a map and direct visitors to their next destination is why they are termed navigation links. 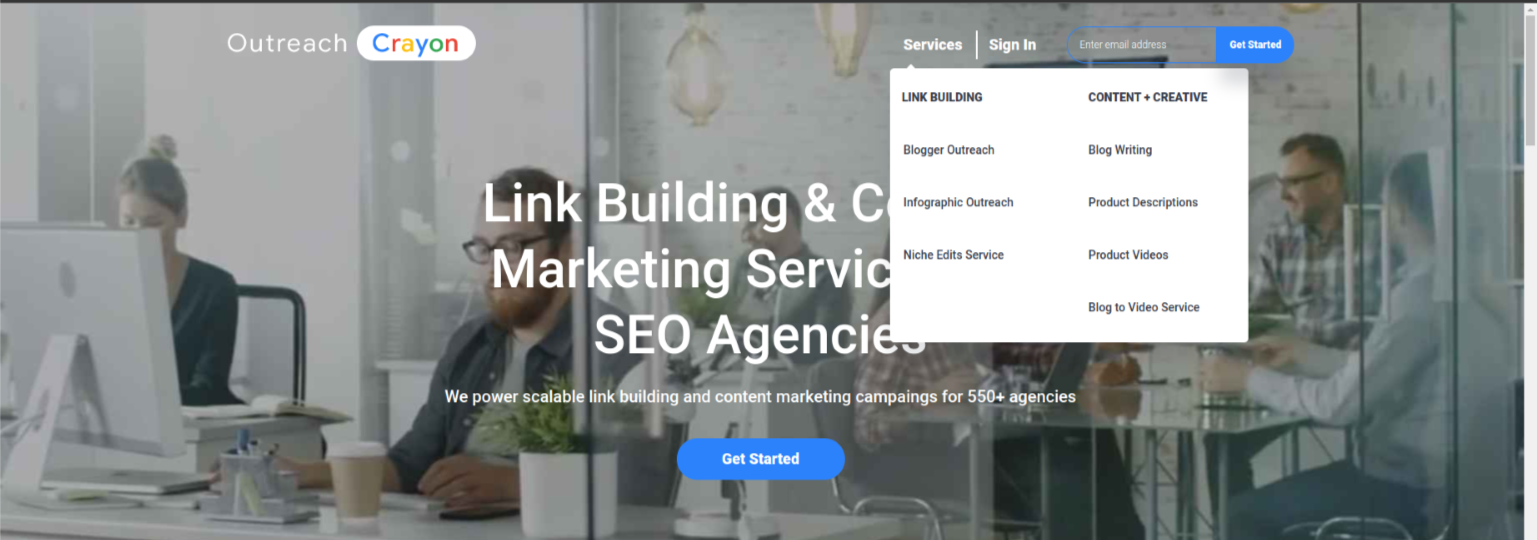
For example, suppose you search for infographic outreach services on Outreach Crayon. The navigational link will work in the following way: Home>Services>Infographic Outreach Each hyperlink you encounter on your path is an internal navigation link that guides you closer to your objective.
2.Contextual Links
Users can discover more relevant information by exploring similar articles or pages through contextual links that are seamlessly integrated into the content. These links, when inserted thoughtfully throughout the text, enhance the reader’s experience by providing pertinent information at just the appropriate times, leading to a thorough comprehension of the subject matter.
It connects people to a greater comprehension of the subject by weaving a web of knowledge inside the text.
Internal links such as the one above can appear in a blog, for instance. Links to other pages are frequently included in the instructional anchor text. Through contextual links, visitors can examine a variety of pertinent and related content, enhancing their experience and piquing their interest in further research.
3.Footer Links
Footer links behave consistently when a visitor navigates across your website’s pages, much like navigation links do. They ought to include links to other significant pages on your website that the user may find useful.
You want your internal links to be in the footer so that if the user hasn’t discovered what they’re searching for by the time they scroll to the end of the page, they can click on another link. Frequently seen links at the bottom of webpages include contact us, help, about pages, frequently asked questions, and similar resource-type pages.
4.Image Links
Charts, infographics, and button pictures are examples of visuals that can function as clickable links. Readers benefit from this strategy, particularly when there is a connected page with more information about the image. This improves the user experience and creates a smooth transition to more in-depth content.
5.In-text Links
Text links in your content are words or phrases that are hyperlinked. Often, the text link has an underlining and is displayed in blue. When it comes to internal linking in SEO strategies, this is the most common kind of link. In-text internal links relate to pertinent content that the user can access at their convenience rather than indicating significance or providing navigation. 
For example, in the above image, “8.4 million websites” and “power of backlinks” are in-text links, which further entice readers to click on them for further information.
Benefits of Internal Links
The numerous benefits of integrating your websites together are listed below.
- Boost to SEO
Internal link structure plays a major role in the structure and search engine ranking of an effective website. They help search engine crawlers understand how your information is prioritized and organized by serving as a guidebook for them. Employing internal links is a wise way to up your SEO game, according to 51% of marketers who recommend including two or three internal links in each article.
Users will have a better experience navigating the website, and your website will witness a higher ranking in search results. It’s similar to making a labeled map of your website that shows search engines where to go and highlights the significance of different content components. 
A thoughtfully crafted internal link within your content improves Google’s understanding of the context of your pages and boosts its ranking in search results.
- Page Authority Distribution
Internal links are a means of allocating authority and ranking power among the many pages on your website. When carefully deployed to connect to important sites, you have the ability to influence which information is more important in search results.
Search engines will give essential sites the attention they deserve because of the dynamic utilization of internal links in creating your website’s hierarchy of significance. By passing information through these internal channels, you can build authority and ultimately enhance your website’s overall effect.
- Enhances Crawlability
Google bots “crawl” your website to discover the subject matter of your content. It is easier for search engines to find pages on your website when you have internal links. It is simpler for Google to carry out the navigation if you have internal links on one page, on the following page, and so on.
You can give crawlers an easy method to find and index new information by providing internal links to newly updated or high-traffic pages from regularly scanned sites. In doing so, the updated or new pages are indexed more rapidly and show up in search results more immediately.
Role of Internal Links in SEO
Now let’s examine the part internal links play in a website’s SEO strategy:
- Improved Site Navigation: It gives structure and logic to your website, making it efficient for search engines and users to navigate. When deciding on page ranking, search engines consider the improved user experience.
- Content Relevance: When there are internal links on your website, search engines can better comprehend the relationships and context between various pages. This deeper comprehension helps your content be better indexed and ranked, particularly for relevant search phrases.
- Distributed Page Authority: Building internal connections to significant pages allows you to disperse authority and ranking power throughout your website. Many pages will benefit from your website’s overall SEO strength as a result.
- Reduced Bounce Rates: When internal linking is done correctly, it lowers bounce rates by encouraging users to browse more pages. Lower bounce rates are a sign that consumers are finding the content worthwhile, which is how search engines perceive them.
- Facilitates Indexing: The paths established by internal links make it efficient for search engine crawlers to find and index fresh content. To make certain that search engines crawl new sites or modifications promptly, this is particularly crucial.
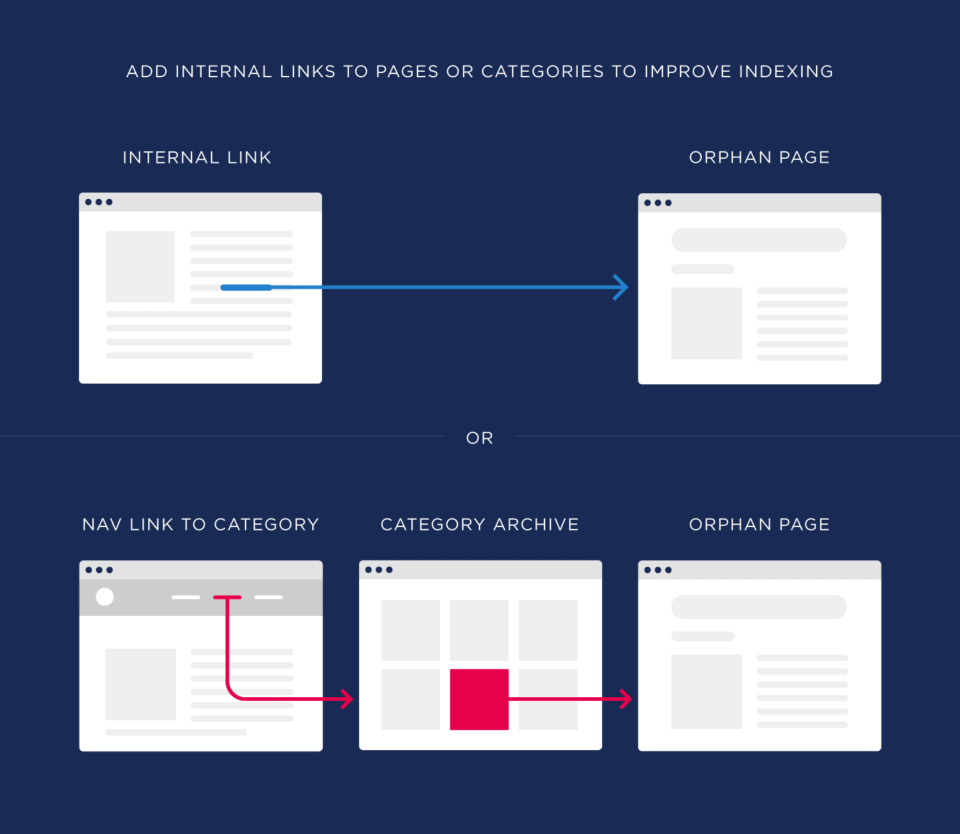
Internal links let Google find pages on your website more easily. It helps especially with the so-called “Orphan pages,” which are pages that are tucked away in the layout of your website. Use your website’s navigation to make an internal link to a page or to its category in order to have a group of pages indexed.
- Keyword Optimization: The use of descriptive anchor text in internal links is one way to optimize for certain keywords. This enhances the ranking of search engines by giving them more context about the content on the connected pages.
The Ideal Count of Internal Links Per Page
The ideal number of internal links on each page depends on several factors, including user experience, website design, and search engine optimization objectives. Although there isn’t a single solution that works for everyone, there are certain things to consider. Aim for two or three internal links on average per page while following SEO best practices. Existing pages have a better chance of ranking higher in the SERPs when you ping them with a new link. When readers follow internal links, they are effectively “refreshing” your older content by telling search engines that it still has value. 
According to Databox, 51% of SEOs believe that bloggers should insert two to three internal links in a blog post, while 36% believe that bloggers should include three to five. Avoiding stuffing the content with too many links is important. Around 150 links per page is the maximum number that search engine crawlers will crawl, according to Moz.
Link stuffing might be detrimental to the search engine optimization of your website. Finding the ideal balance necessitates constant optimization, making sure that the content is relevant, and preserving high standards. It’s a dynamic process that changes as your website’s content changes and search engine algorithms change over time.
Key Difference: External Vs. Internal Links
Now, let’s examine the distinctions between internal and external links and their distinct functions within an all-encompassing link-building approach.
| Criteria | External Links | Internal Links |
| Definition | Are hyperlinks that lead from one website’s page to another’s page | Hyperlinks that provide a connection between two pages on the same website |
| Purpose | Users are directed to information sources on different domains using external links | Search engines and users can find related information within the same site by using internal links |
| SEO Impact | Extremely important for backlink profiles and search engine rankings | Enhances the user experience and architecture of websites, which aids in SEO initiatives |
| Control | Since your content is dependent upon other websites for connectivity, control is limited | Total control that can be wisely positioned within a website’s content |
| Authority | A website’s authority is increased via external links from reliable websites | Complete authority that can be deliberately put into a website’s content |
| Relevance | Must be logical in light of the circumstances and the data on the associated page | On the same website, readers should be guided to relevant and helpful content |
| User Experience | Enables users to access other resources and references | Gives users improved navigation to make finding stuff easier |
Internal Linking Best Practices
To make the most of internal links, bear in mind the following recommended tactics:
- Relevance is Key: Since relevance is important, make sure the internal links you use make sense. Visitors should be able to access related websites or more content on the same subject through connectivity.
- Hierarchy and Structure: Clearly define the hierarchy and structure of your internal links. You can facilitate easier site navigation by prioritizing vital pages and maintaining a consistent site flow.
- Limit the Number: Despite their value, internal links should not be used excessively in your writing. Provide something of value to the user and prioritize quality above quantity.
- Fix Broken Links: Examine and update internal links often. In addition to negatively affecting SEO, broken links detract from the user experience.
- Strategic Placement: Throughout the content, carefully place internal links to direct users to appropriate and relevant pages without interfering with their reading experience.
Final Thoughts
In order to meet the objectives of search engine optimization and user experience, it is crucial to carefully analyze the number of internal links on a page. Although there isn’t a set ratio, it’s generally recommended to strive for five to ten internal links for every 2,000 words of content.
Restricting the number of connections one creates is essential since Google will not index a page with more than 150 links. It is important to find the proper balance, avoid utilizing too many links, and monitor the caliber of your internal linking in order to guarantee that people can easily access your content. To choose the best internal linking strategy, quality, and relevance must be prioritized.

About the author: Vibhav Gaur, Business Head
Vibhav Gaur leads strategic operations and business growth at the organization. With a strong background in digital transformation and customer-focused solutions, he has helped numerous clients streamline their web presence and scale efficiently. His leadership ensures seamless execution across teams, with a commitment to delivering results and fostering innovation in every project.